author:hydro-thermally oxidizing Snnanoparticles in glucose solution. Structural characterizations using SE time:2016-09-28
Chestnut-like SnO2 and SnO2/C nanocomposites withhierarchical structures are synthesized by hydro-thermally oxidizing Sn nanoparticles in glucose solution. Structural characterizations using SEM and TEM reveal that the SnO2 nanoparticles arecomposedofnumerous, randomly arranged SnO2 nanosheets with hollow cores. Owing to the short electron and ion diffusion distances and transformation strainac-commodation mechanism of this structure the new SnO2/C nanocomposites exhibit enhanced lithium ion storage properties with a capacity of �930 mAhg�1 and capacity retention of about 96% after 100 cyclesat 0.1C.An in situ TEM stud yof the electrochemically driven lithiation/delithiation of SnO2/C nanocomposites reveals that their enhanced cyclingstability is mainly facilitated by the limited volume expansion and excellent mechanical robustness of the hollow chestnuts.
近年来,随着电子产品和电动汽车的快速发展,其对锂离子电池的能量密度也提出了更高的要求。二氧化锡作为一种高比容量的负极材料,其理论容量达到了商用石墨负极材料的2倍以上,具有很好的应用前景。但二氧化锡在嵌锂/脱锂的过程中伴随着约250%的体积膨胀和收缩,使得二氧化锡纳米材料在数个循环之后就粉化、脱落,从而造成电池容量的快速衰减,严重限制二氧化锡在锂离子电池中的应用。
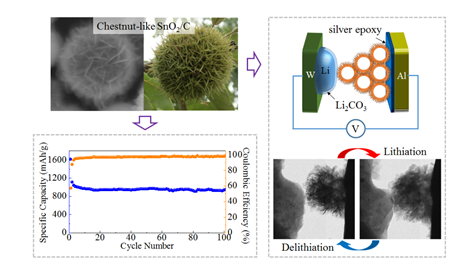
为了解决容量衰减这个核心问题,西安交大材料学院微纳中心博士生杨烈在导师宁晓辉副教授的指导下,对二氧化锡的形貌进行了设计和调控,采用了简单易行的水热反应方法,成功合成出了具有板栗壳状结构的中空二氧化锡纳米颗粒。并采用原位透射电镜技术,对这种特殊结构的二氧化锡进行原位充放电实验。研究发现,这种结构的纳米颗粒在各个方向都有充足的缓冲空间,可以大幅度减小二氧化锡在嵌锂过程中的体积膨胀。此外,通过把板栗状二氧化锡颗粒与碳复合,可有效提高其导电性能。电池电化学性能测试结果表明,这种板栗状的二氧化锡/碳复合纳米颗粒具有很高的充放电容量,并且表现出十分稳定的循环性能。此结果为改进锂离子电池负极材料的结构设计提供了研究思路。
该成果近日在线发表在材料科学领域知名期刊《Nano Energy》上(影响因子11.553),西安交通大学是第一作者与第一通讯单位。参与该工作的还有解德刚博士、卡内基梅隆大学R. Lakshmi Narayan博士以及微纳中心的博士生王悦存和代涛。该研究得到了国家自然科学基金(51401157)和陕西省基础科学研究基金(2015JQ5164)的支持。
文章链接:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211285516303573

